Setup staging environment for backend
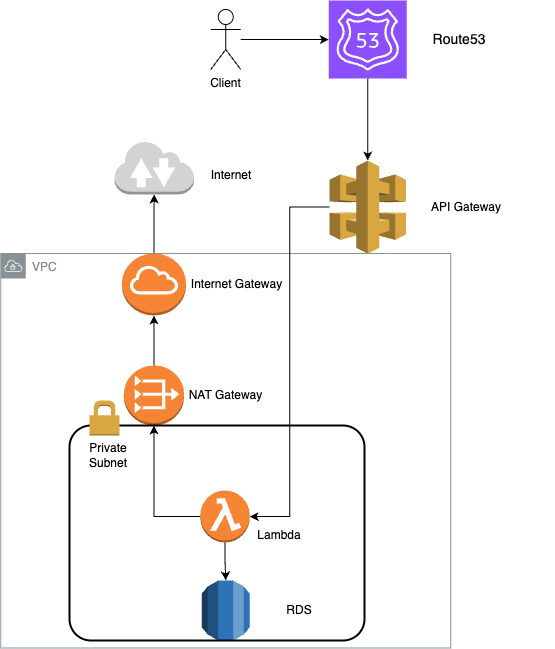
API Gateway → Lambda → RDS
The way to host backend with fastapi is to first put your fastapi app on lambda and then connect it to an api gateway which would handle the requests.
_init.tf
provider "aws" {
region = var.region
}
_variables.tf
variable "build_hash" {
description = "The tag of the Docker image to use for the Lambda function"
type = string
}
variable "account_id" {
description = "The AWS account ID"
type = string
}
variable "region" {
description = "The AWS region to deploy to"
type = string
}
variable "password" {
description = "The password for the RDS instance"
type = string
}
variable "db_name" {
description = "The name of the database"
type = string
}
variable "username" {
description = "The username for the RDS instance"
type = string
}
variable "project_name" {
description = "The name of the project"
type = string
}
Remote states here are used to retrieve outputs of other terraform modules/resources. Here in particular vpc details like vpc_id etc can be obtained.
_remote_state.tf
data "terraform_remote_state" "vpc" {
backend = "s3"
config = {
bucket = "campus-space-terraform-state-staging"
key = "campus-space/cloud/infra"
region = "ap-south-1"
}
}
Terraform needs to store its state. Meaning it needs to know the updates that the resouces have gone through. so terraform uses a state file. Without this terraform will be out of sync. Currently I have stored the state file in another s3 bucket and referenced the url because storing it remotely is better than local.
backend.tf
terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "campus-space-terraform-state-staging"
key = "campus-space/cloud/terraform-backend.tfstate"
region = "ap-south-1"
}
}
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that helps you securely control access to AWS resources. With IAM, you can manage permissions that control which AWS resources users can access. You use IAM to control who is authenticated (signed in) and authorized (has permissions) to use resources.
iam.tf
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_execution_role" {
name = "lambda_execution_role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "lambda.amazonaws.com"
}
},
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "lambda_vpc_access" {
name = "lambda-vpc-access"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_execution_role.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = [
"ec2:CreateNetworkInterface",
"ec2:DescribeNetworkInterfaces",
"ec2:DeleteNetworkInterface"
],
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "lambda_execution_policy" {
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_execution_role.name
}
The api gateway here acts as a entrypoint for all the http requests sent to my lambda.Hence the custom domain is also attached to it.
agw.tf
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_api" "lambda_api" {
name = "${var.project_name}-api"
protocol_type = "HTTP"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "lambda_integration" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_api.id
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY"
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.campus_lambda.invoke_arn
integration_method = "POST"
payload_format_version = "2.0"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_route" "lambda_route" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_api.id
route_key = "ANY /{proxy+}"
target = "integrations/${aws_apigatewayv2_integration.lambda_integration.id}"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_stage" "default" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_api.id
name = "$default"
auto_deploy = true
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_apigw_invoke" {
statement_id = "AllowAPIGatewayInvoke"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.campus_lambda.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = "${aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_api.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_domain_name" "custom_domain" {
domain_name = "staging-api.campusspace.in"
domain_name_configuration {
certificate_arn = "arn:aws:acm:ap-south-1:058264333757:certificate/31709394-a501-4556-9196-6fc968685de1"
endpoint_type = "REGIONAL"
security_policy = "TLS_1_2"
}
}
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_api_mapping" "default_mapping" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_api.id
domain_name = aws_apigatewayv2_domain_name.custom_domain.domain_name
stage = aws_apigatewayv2_stage.default.name
}
The fastapi backend is hosted on lambda.It is inside a private subnet inside a VPC. The image uri needed is obtained after building the backend into a docker image and uploading to ECR.
lambda.tf
resource "aws_lambda_function" "campus_lambda" {
function_name = "${var.project_name}-lambda"
image_uri = "${var.account_id}.dkr.ecr.${var.region}.amazonaws.com/fastapi-lambda:${var.build_hash}"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_execution_role.arn
package_type = "Image"
vpc_config {
subnet_ids = [data.terraform_remote_state.vpc.outputs.private_subnet_id]
security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.lambda_sg.id]
}
environment {
variables = {
DATABASE_URL = "postgresql+asyncpg://${aws_db_instance.lms.username}:${aws_db_instance.lms.password}@${aws_db_instance.lms.endpoint}/${aws_db_instance.lms.db_name}"
}
}
}
rds.tf
resource "aws_db_instance" "lms" {
identifier = "lms-rds"
engine = "postgres"
engine_version = "17.2"
instance_class = "db.t3.micro"
allocated_storage = 20
storage_type = "gp2"
username = var.username
password = var.password
db_name = var.db_name
publicly_accessible = false
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.rds_sg.id]
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.rds_subnet_group.name
skip_final_snapshot = true
deletion_protection = false
}
route53.tf
data "aws_route53_zone" "api" {
name = "staging-api.campusspace.in."
private_zone = false
}
resource "aws_route53_record" "api_domain" {
zone_id = data.aws_route53_zone.api.zone_id
name = "staging-api.campusspace.in"
type = "A"
alias {
name = aws_apigatewayv2_domain_name.custom_domain.domain_name_configuration[0].target_domain_name
zone_id = aws_apigatewayv2_domain_name.custom_domain.domain_name_configuration[0].hosted_zone_id
evaluate_target_health = false
}
}
sg.tf
resource "aws_security_group" "lambda_sg" {
name = "${var.project_name}-lambda-sg"
description = "Security group for Lambda in VPC"
vpc_id = data.terraform_remote_state.vpc.outputs.vpc_id
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "rds_sg" {
name = "postgres-rds-sg"
description = "Allow Lambda to access RDS"
vpc_id = data.terraform_remote_state.vpc.outputs.vpc_id
ingress {
from_port = 5432
to_port = 5432
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/16"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
subnet_rds.tf
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "rds_subnet_group" {
name = "${var.project_name}-rds-subnet-group"
subnet_ids = [
data.terraform_remote_state.vpc.outputs.private_subnet_id,
data.terraform_remote_state.vpc.outputs.public_subnet_id,
]
}